Phone Number
(+91) 8655358999
To accurately control process temperature without extensive operator involvement, a temperature control system relies upon a controller, which accepts a temperature sensor such as a thermocouple or RTD as input. It compares the actual temperature to the desired control temperature, or set point, and provides an output to a control element. The controller is one part of the entire control system, and the whole system should be analyzed in selecting the proper controller.
The ON/OFF controller switches the output when the setpoint is reached. If the value falls below the setpoint by a certain adjustable tolerance (xsd, switching differential, hysteresis), then the output is switched on again. It therefore only has two switching states. It is used in temperature control applications where the heating or cooling is only switched on or off. A 2-state controller with dynamics can, however, also operate with a P, I, or D component.
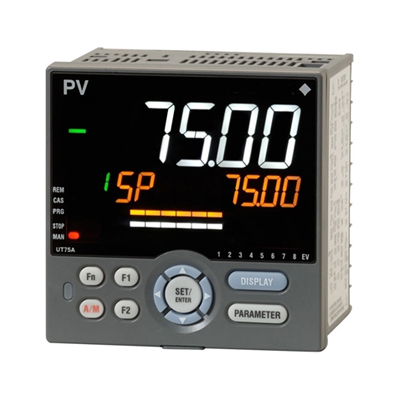

Control of temperatures, pressures, and other process variables
Single loop controllers are used to control a thermal or process machine in systems which need a single control loop or discrete devices.
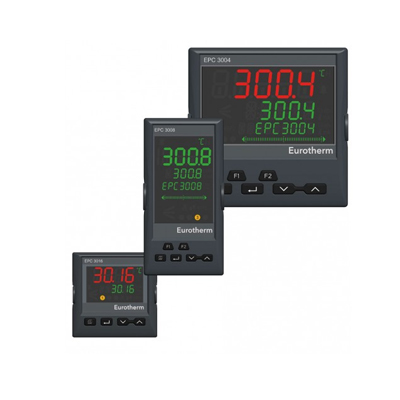

Multiple Process Plants
Multi-loop temperature controllers manage several zones simultaneously to stabilize the temperature of environments such as ovens, packaging, and heat treatment. Generally, behind panel, multi- loop controllers support various fieldbus options allowing for easy integration with other devices within the machine or a wider plant network. Multi ŌĆō loop systems can be programmed to allow the zones to be independent or to work in conjunction with one another, depending on the needs of the application. Benefits of the multi ŌĆō loop temperature controller includes reduced installation costs, improved integration and minimal machine downtime.

Continuous bottle filling system, Batch mixing system, stage air conditioning system, Traffic control
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) also known as Industrial Computer is the major component in the industrial automation sector. Due to its robust construction, exceptional functional features like PID controllers, sequential control, timers and counters, ease of programming, reliable controlling capabilities and ease of hardware usage ŌĆō this PLC is more than a special-purpose digital computer in industries as well as in other control-system areas.

Continuous bottle filling system, Batch mixing system, stage air conditioning system, Traffic control
Distributed Control System is most popular which is specially designed with redundancy and diagnostic capabilities to improve control reliability and performance. It gives greater flexibility to control distributed discrete field devices and its operating stations
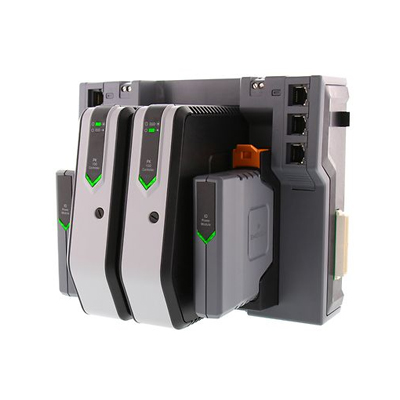

Chemical plants, Petrochemical (oil) and refineries, Pulp and Paper Mills, Boiler controls and power plant systems, Nuclear power plants, Environmental control systems, Water management systems, Water treatment plants, Sewage treatment plants
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) refers to industrial control systems (ICS) that are employed to control and keep track of equipment or a plant in industries like water and waste control, telecommunications, energy, transport, and oil and gas refining. SCADA is a computer system used to gather and analyze real-time data. This data is processed by the computer and is presented on a regular basis. SCADA also saves and make logs for every event into a log file that is saved on a hard drive or is sent to a printer. SCADA gives warnings by sounding alarms if situations develop into hazardous scenarios.
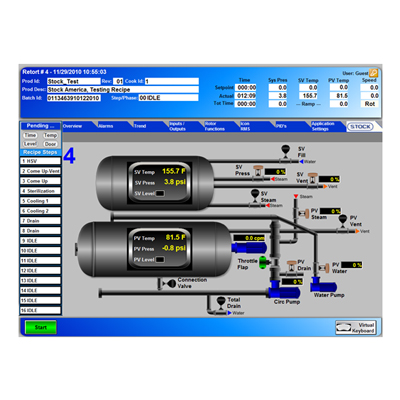
SCADA systems are used for monitoring a variety of data like flows, currents, voltages, pressures, temperatures, water levels, and etc., in various industries. If the system detects any abnormal conditions from any monitoring data, then the alarms at the central or remote sites will be triggered for alerting the operators through HMI. There are numerous applications of SCADA systems, but a few most frequently used SCADA applications include: